- Hot
- Portable
- Countertop
- miniPOS
- Retail PIN Pad
- Smart ECR
- Unattended
- QR Payments
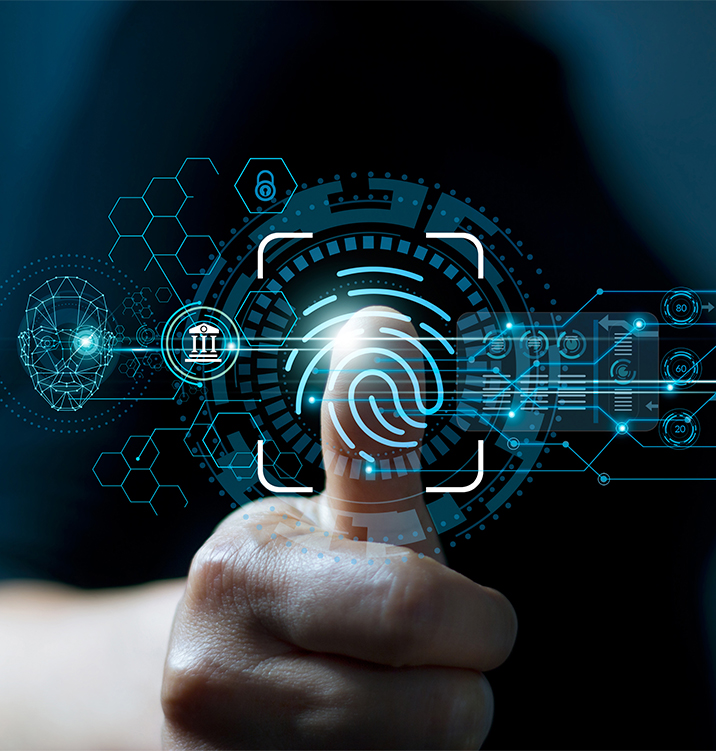
































































Biometric technology—once limited to high-security environments—has entered everyday consumer life, now embedded in smartphones, laptops, airport gates, and increasingly, payment terminals. The payments industry is undergoing a profound shift, with biometrics such as fingerprints, facial recognition, and palm-vein scans rapidly becoming central to how people authenticate transactions. This transformation is driven by a convergence of security demands, convenience expectations, operational pressures, and digital-first consumer behavior.
While mobile biometrics took off with platforms like Apple Pay and Samsung Pay, the next wave is happening at the physical point of sale. Retailers, banks, and payment technology providers are increasingly experimenting with biometric-enabled terminals that authenticate customers with a touch or a glance. As adoption spreads, biometrics promises major gains—but not without risks and complexities.
Security is the most compelling driver for biometric adoption. Traditional authentication methods—PIN codes, signatures, passwords—are no longer sufficient in an era of sophisticated fraud schemes. Biometrics, tied directly to the user's unique physical characteristics, offer a far stronger layer of authentication.
Fingerprints and facial recognition drastically reduce the risk of stolen credentials, card skimming, or account takeover. When a consumer authorizes a payment with a biometric check, the possibility of an imposter completing the transaction falls dramatically. This is especially impactful at unattended terminals such as kiosks or self-checkout stations, where fraud attempts are historically higher.
Tokenization and on-device processing, used widely in biometric systems, further enhance security by ensuring that sensitive biometric data never leaves the user’s device or is never transmitted in raw form. As fraud continues to rise globally, merchants and payment service providers see biometrics as a way to close critical security gaps.
Beyond security, convenience is the main reason consumers embrace biometric payments. With a simple tap of a finger or quick facial scan, the authentication process becomes almost instantaneous. This eliminates the need to remember PINs, manage multiple cards, or fumble with devices at checkout.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the appetite for contactless experiences. While NFC cards and mobile wallets delivered significant improvements, biometrics push convenience further, enabling:
Consumers increasingly expect payment experiences to be faster and more frictionless. Biometrics deliver exactly that.
For businesses, the economic case for biometrics is becoming stronger each year. Fraud remains a major operational cost for merchants and financial institutions, and biometric authentication dramatically reduces false transactions.
Lower fraud costs translate into:
Biometrics also encourage customers to participate more actively in digital ecosystems. For example, mobile banking usage typically rises significantly when biometric login is enabled, because the barrier to entry—typing a password—is removed. The same trend appears in retail and e-commerce environments: once users grow comfortable with biometric authentication, they are more likely to use digital payment channels.
Retailers deploying biometric terminals also benefit from improved customer throughput and potentially higher sales volumes due to reduced friction at checkout.
In high-volume retail environments—supermarkets, transportation hubs, quick-service restaurants—transaction speed is critical. Biometrics reduce the need for manual steps such as entering PIN codes or presenting identification for certain purchases.
This enables:
Biometric systems at payment terminals can authenticate a user in a fraction of a second. The cumulative impact on customer flow is substantial, especially in stores processing thousands of transactions per day.
Retailers are also adopting biometrics for back-office functions, such as employee clock-ins or access control, creating operational efficiencies beyond customer payments.
Despite the advantages, biometric payment systems come with higher privacy risks if data is not managed securely. Unlike passwords, biometric traits cannot be changed. If a fingerprint template or facial scan is compromised, the implications are far more serious and long-lasting.
Key risks include:
Therefore, robust data governance is essential. Leading payment providers use:
As adoption increases, regulators are paying closer attention, establishing guidelines on how biometric data should be stored, processed, and deleted.
Biometric authentication is growing rapidly across mobile and e-commerce channels. Smartphone penetration—with devices like the iPhone and many Android models—has made biometrics familiar and trusted by billions of users worldwide.
E-commerce platforms increasingly support biometric logins, enabling secure one-touch checkout using stored payment details. Mobile banking apps depend heavily on biometrics, accelerating their adoption.
However, adoption at payment terminals—the focus of the next major growth phase—is more uneven. Factors influencing this include:
Early adoption is strong in Asia and parts of Europe, where digital payments are mature and regulatory support is clearer. The United States is moving steadily, with several major retailers and payment providers piloting biometric checkout systems.
Biometrics are poised to become a standard authentication layer in the global payment ecosystem. As consumers grow more comfortable using fingerprints and facial recognition for everyday tasks, biometric checkout at physical terminals will feel like a natural extension of digital experiences.
The industry is moving toward a future where a customer can walk into a store, select items, and authenticate their payment with a quick biometric confirmation—no wallet, card, or phone required.
In summary, the rise of biometrics in payments reflects a broader trend toward seamless, secure, and digital-first commerce. With strong advantages in security, convenience, and efficiency, biometric payments are rapidly expanding across sectors, though adoption remains uneven and privacy concerns must be carefully managed. As the technology matures, it will redefine how people interact with both digital and physical payment environments, shaping the future of commerce for years to come.
 Back
Back





